How To Create A File In Bash Script
One of the essential tasks we do while working with bash scripting is reading and writing files. In this guide, we will focus on how to read files in bash and how to edit them.
There are multiple ways to read and write a file in bash. The simplest way is using operators ">" and ">>".
- ">" operator will overwrite the existing data
- ">>" operator will append data
The general format of using redirection operators is:
Data > File Name
Data >> File Name
Let's understand the writing to a file procedure with an example:
How to write a file using redirection operators
As discussed above, the simple and straightforward approach of writing to a file is using redirection operators. For instance, if you want to change the text of an already existing file, then firstly create a text file by the name of "testfile.txt" and write anything in it:
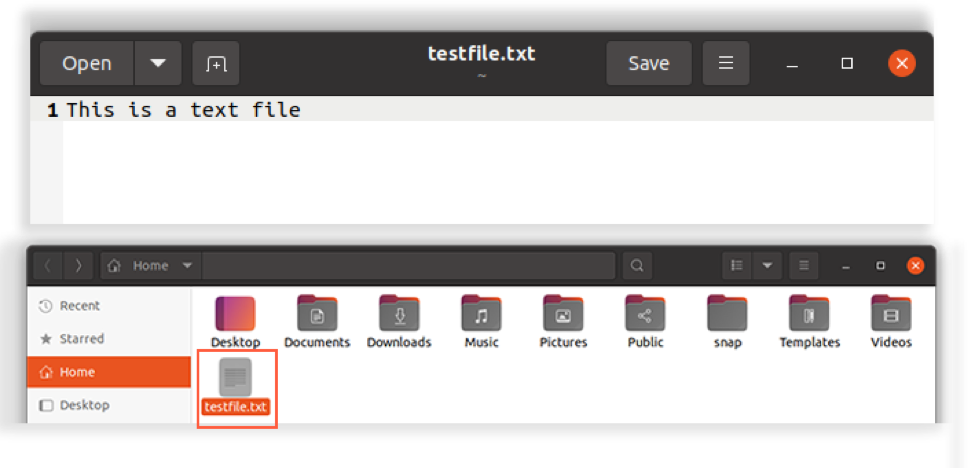
Save the text file.
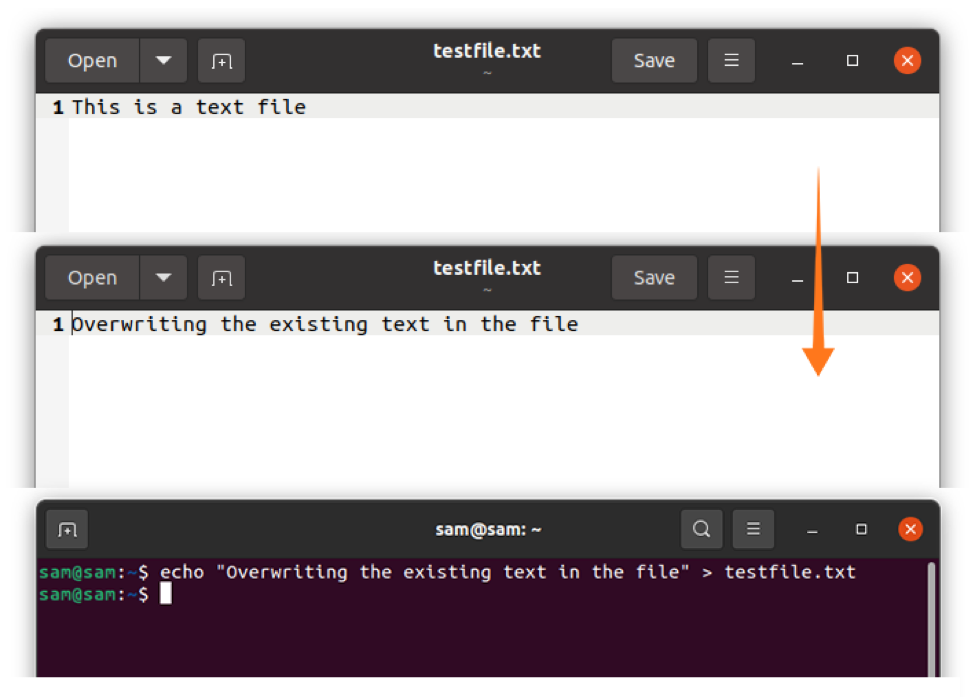
Type the below-mentioned command in the terminal:
$ echo "Overwriting the existing text in the file" > testfile.txt
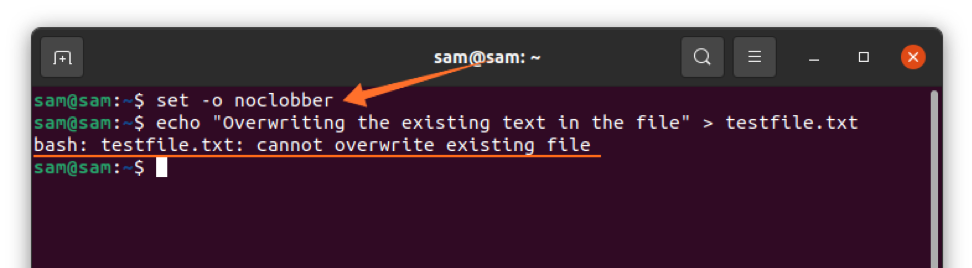
Over wring may be risky; therefore, it is good practice to enable "noclobber". Setting "noclobber" would block any overwriting to any exiting file.
$ set –o noclobber
$ echo "Overwriting the existing text in the file" > testfile.txt
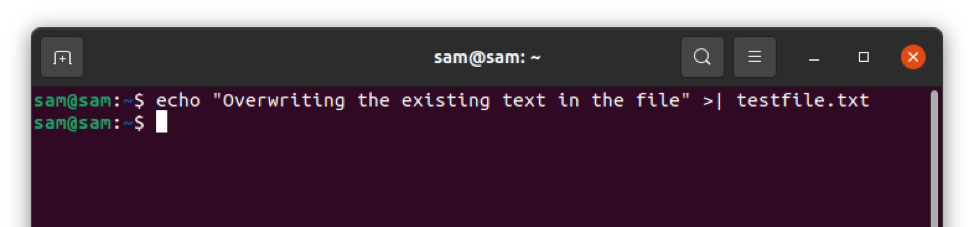
But if you want to bypass "noclobber" then use the">|" operator instead of ">":
$ echo "Overwriting the existing text in the file" >| testfile.txt
Or you can simply disable "noclobber":
But this command will take away protection from all the files.
The above output is indicating that the existing text has been overwritten. Now, let's use the ">>" operator:
$ echo "Appending text to the existing text file" >> testfile.txt

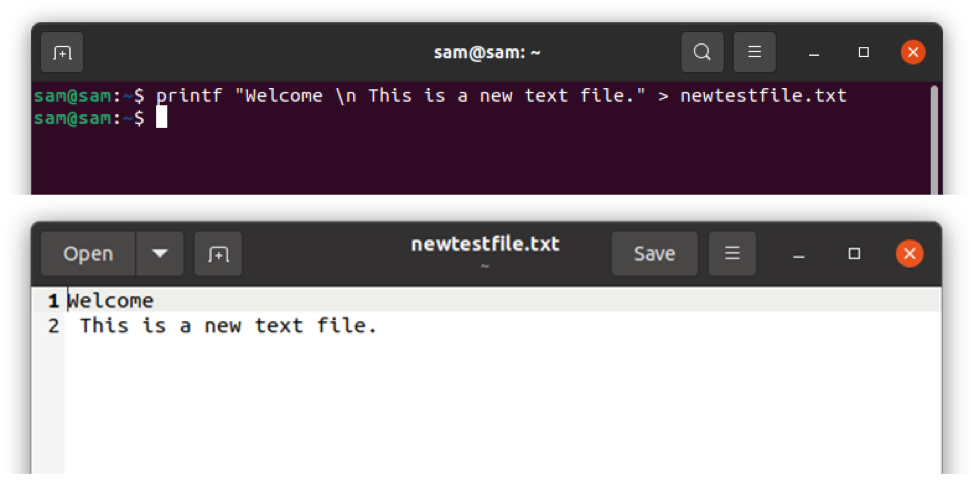
"echo" is not always ideal to use since you cannot format text using it, therefore use "printf" in the place of "echo" to format the text as demonstrated in the following command:
$ printf "Welcome \n This is a new text file." > newtestfile.txt
Let's understand the concept with a bash script example. Open Vim by typing "vim" in the terminal. If you do not have Vim editor on your device, then install it using:
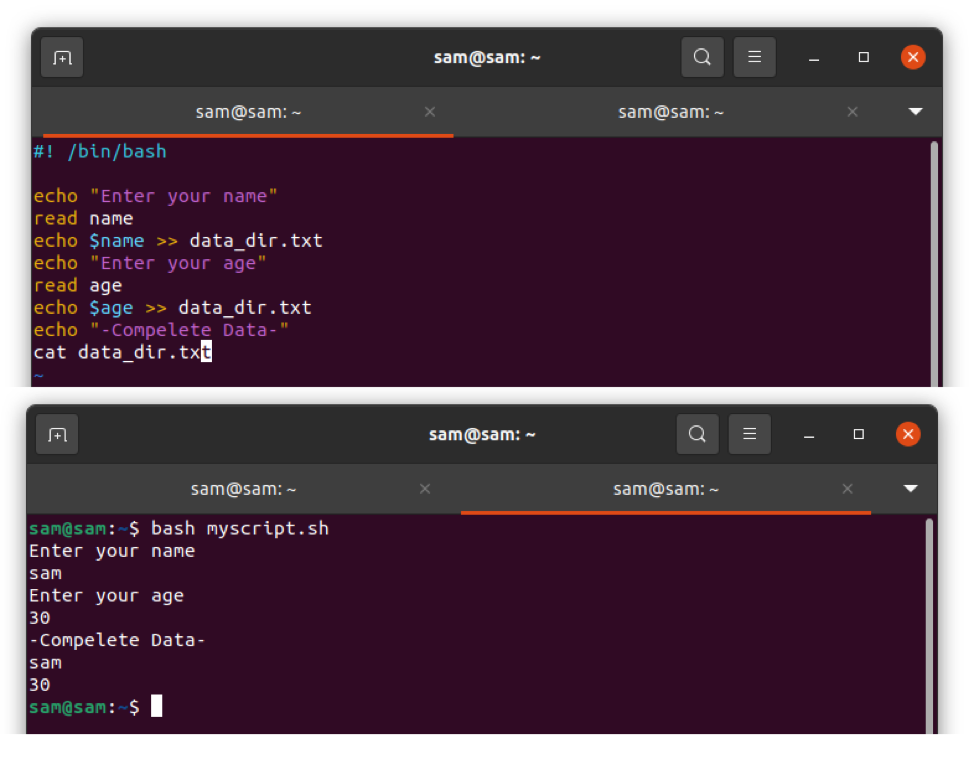
Type the script:
#! /bin/bash
echo "Enter your name"
read name
echo $name > data_dir.txt
echo "Enter your age"
read age
echo $age >> data_dir.txt
cat data_dir.txt
The "cat" command is used to create and edit the files. Save the above script in Vim by switching mode after pressing the "Esc" key and then type ":w myscript.sh". Open the terminal and run the code:
How to write a file using Heredoc
If you want to write multiple lines, then the easiest method is using "Heredoc". Here document, also known as "Heredoc," is a multi-purpose code block. The syntax of Heredoc is:
Command <<[-] Delimiter
.
text/commands
.
Delimiter
Any string can be used in the place of "Delimiter", and "-" can also be used to remove any tab spaces in the file. Let's understand it using a simple example:
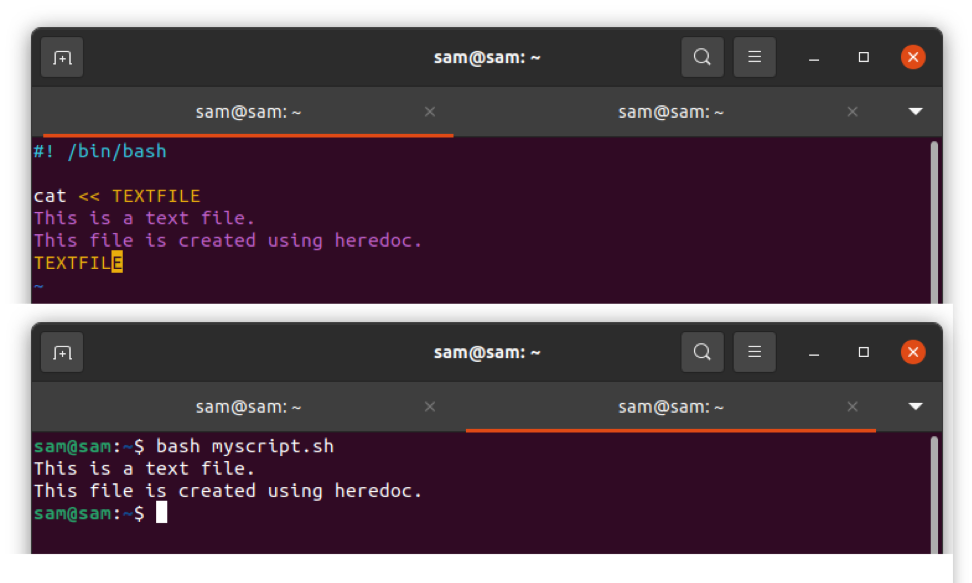
#! /bin/bash
cat << TEXTFILE
This is a text file.
This file is created using heredoc.
TEXTFILE
The above script "cat" command creates a text file by the name of "TEXTFILE," and writing text into the file just created. Now save the file by the name of "myscript.sh". Launch terminal and run the script.
How to write a file using the Tee command
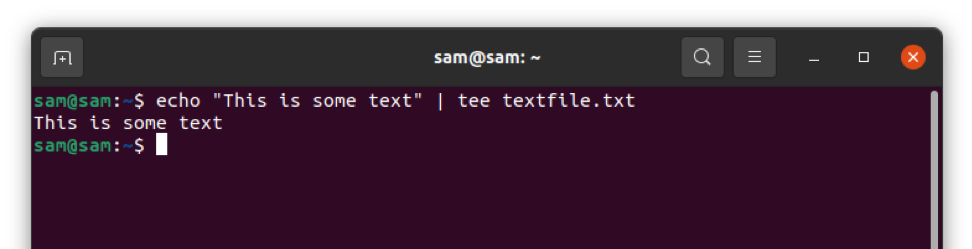
Another method to write a file is using the "Tee" command. As name indicating this command takes input and writes to a file and shows output simultaneously. By default, the "Tee" command will overwrite the existing data.
$ echo "This is some text" | tee textfile.txt
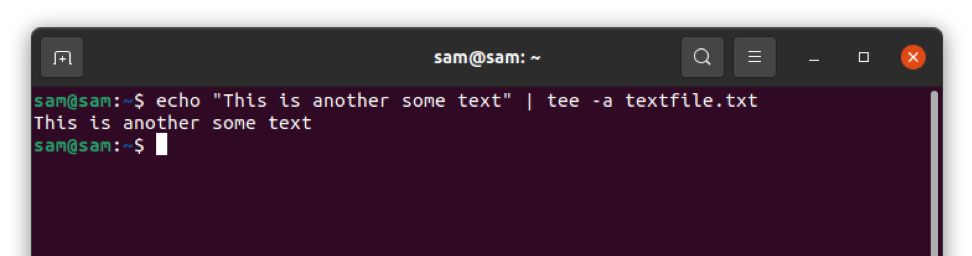
To append use –a:
$ echo "This is another text" | tee –a textfile.txt
To write multiple lines, use:
$ echo "Adding text to multiple files" | tee textfile1.txt textfile2.txt textfile3.txt
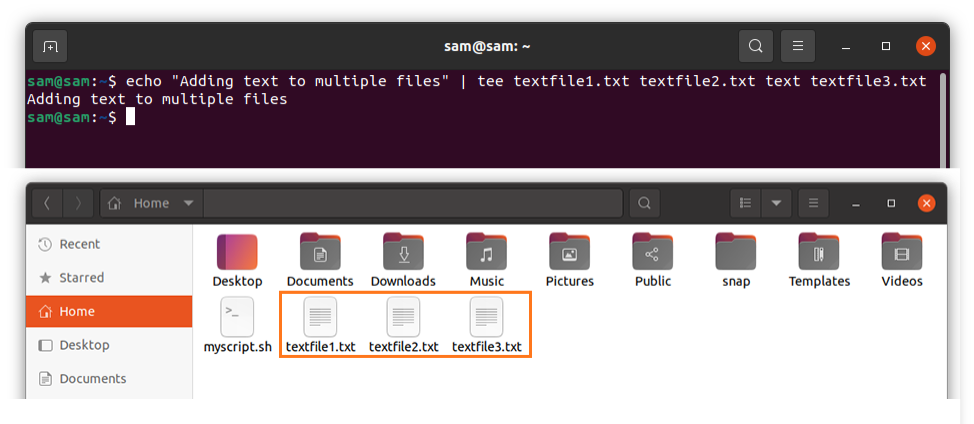
The above command will create three files if they are not existed and write text to each of them.
Conclusion
This guide is focusing on multiple approaches to write to a file in bash with examples. In bash scripting, there are multiple ways to write a file, but the simplest one is using redirection operators ">", ">>". To write multiple lines, "heredoc" can be used, and if you want to write the same data to multiple lines, then the "tee" command is quite handy.
About the author

I am a professional graphics designer with over 6 years of experience. Currently doing research in virtual reality, augmented reality and mixed reality.
I hardly watch movies but love to read tech related books and articles.
How To Create A File In Bash Script
Source: https://linuxhint.com/write-to-file-bash/
Posted by: vangentler63.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Create A File In Bash Script"
Post a Comment