How To Create Static Variable In Java
static is a non-access modifier in Java which is applicable for the following:
- blocks
- variables
- methods
- nested classes
To create a static member(block,variable,method,nested class), precede its declaration with the keyword static. When a member is declared static, it can be accessed before any objects of its class are created, and without reference to any object. For example, in below java program, we are accessing static method m1() without creating any object of Test class.
Attention reader! Don't stop learning now. Get hold of all the important Java Foundation and Collections concepts with the Fundamentals of Java and Java Collections Course at a student-friendly price and become industry ready. To complete your preparation from learning a language to DS Algo and many more, please refer Complete Interview Preparation Course .
class Test
{
static void m1()
{
System.out.println( "from m1" );
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
m1();
}
}
Output:
from m1
Static blocks
If you need to do computation in order to initialize your static variables, you can declare a static block that gets executed exactly once, when the class is first loaded. Consider the following java program demonstrating use of static blocks.
class Test
{
static int a = 10 ;
static int b;
static {
System.out.println( "Static block initialized." );
b = a * 4 ;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println( "from main" );
System.out.println( "Value of a : " +a);
System.out.println( "Value of b : " +b);
}
}
Output:
Static block initialized. from main Value of a : 10 Value of b : 40
For Detailed article on static blocks, see static blocks
Static variables
When a variable is declared as static, then a single copy of variable is created and shared among all objects at class level. Static variables are, essentially, global variables. All instances of the class share the same static variable.
Important points for static variables :-
- We can create static variables at class-level only. See here
- static block and static variables are executed in order they are present in a program.
Below is the java program to demonstrate that static block and static variables are executed in order they are present in a program.
class Test
{
static int a = m1();
static {
System.out.println( "Inside static block" );
}
static int m1() {
System.out.println( "from m1" );
return 20 ;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println( "Value of a : " +a);
System.out.println( "from main" );
}
}
Output:
from m1 Inside static block Value of a : 20 from main
Static methods
When a method is declared with static keyword, it is known as static method. The most common example of a static method is main( ) method.As discussed above, Any static member can be accessed before any objects of its class are created, and without reference to any object.Methods declared as static have several restrictions:
- They can only directly call other static methods.
- They can only directly access static data.
- They cannot refer to this or super in any way.
Below is the java program to demonstrate restrictions on static methods.
class Test
{
static int a = 10 ;
int b = 20 ;
static void m1()
{
a = 20 ;
System.out.println( "from m1" );
b = 10 ;
m2();
System.out.println( super .a);
}
void m2()
{
System.out.println( "from m2" );
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
}
}
When to use static variables and methods?
Use the static variable for the property that is common to all objects. For example, in class Student, all students shares the same college name. Use static methods for changing static variables.
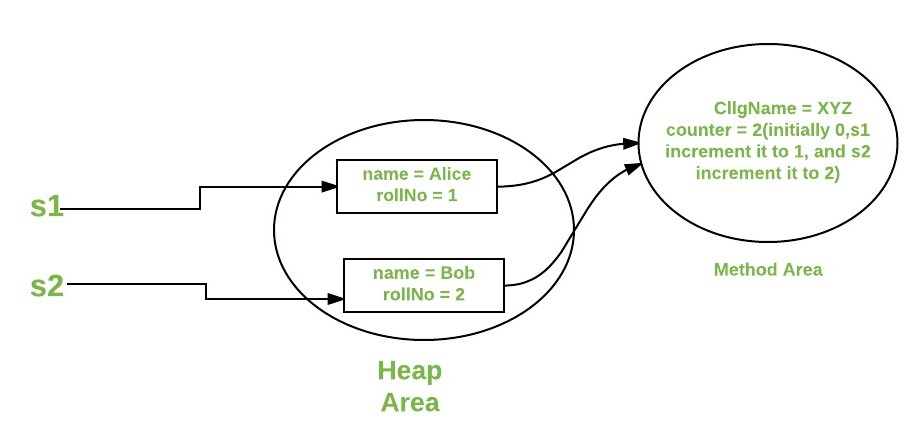
Consider the following java program, that illustrate the use of static keyword with variables and methods.
class Student
{
String name;
int rollNo;
static String cllgName;
static int counter = 0 ;
public Student(String name)
{
this .name = name;
this .rollNo = setRollNo();
}
static int setRollNo()
{
counter++;
return counter;
}
static void setCllg(String name){
cllgName = name ;
}
void getStudentInfo(){
System.out.println( "name : " + this .name);
System.out.println( "rollNo : " + this .rollNo);
System.out.println( "cllgName : " + cllgName);
}
}
public class StaticDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Student.setCllg( "XYZ" );
Student s1 = new Student( "Alice" );
Student s2 = new Student( "Bob" );
s1.getStudentInfo();
s2.getStudentInfo();
}
}
Output:
name : Alice rollNo : 1 cllgName : XYZ name : Bob rollNo : 2 cllgName : XYZ
Static nested classes : We can not declare top-level class with a static modifier, but can declare nested classes as static. Such type of classes are called Nested static classes. For static nested class, see static nested class in java
This article is contributed by Gaurav Miglani. If you like GeeksforGeeks and would like to contribute, you can also write an article using contribute.geeksforgeeks.org or mail your article to contribute@geeksforgeeks.org. See your article appearing on the GeeksforGeeks main page and help other Geeks.
Please write comments if you find anything incorrect, or you want to share more information about the topic discussed above.
How To Create Static Variable In Java
Source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/static-keyword-java/
Posted by: vangentler63.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Create Static Variable In Java"
Post a Comment