How To Create One Dimensional Array In Java
Java Arrays
Normally, an array is a collection of similar type of elements which has contiguous memory location.
Java array is an object which contains elements of a similar data type. Additionally, The elements of an array are stored in a contiguous memory location. It is a data structure where we store similar elements. We can store only a fixed set of elements in a Java array.
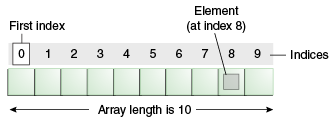
Array in Java is index-based, the first element of the array is stored at the 0th index, 2nd element is stored on 1st index and so on.
Unlike C/C++, we can get the length of the array using the length member. In C/C++, we need to use the sizeof operator.
In Java, array is an object of a dynamically generated class. Java array inherits the Object class, and implements the Serializable as well as Cloneable interfaces. We can store primitive values or objects in an array in Java. Like C/C++, we can also create single dimentional or multidimentional arrays in Java.
Moreover, Java provides the feature of anonymous arrays which is not available in C/C++.
Advantages
- Code Optimization: It makes the code optimized, we can retrieve or sort the data efficiently.
- Random access: We can get any data located at an index position.
Disadvantages
- Size Limit: We can store only the fixed size of elements in the array. It doesn't grow its size at runtime. To solve this problem, collection framework is used in Java which grows automatically.
Types of Array in java
There are two types of array.
- Single Dimensional Array
- Multidimensional Array
Single Dimensional Array in Java
Syntax to Declare an Array in Java
Instantiation of an Array in Java
Example of Java Array
Let's see the simple example of java array, where we are going to declare, instantiate, initialize and traverse an array.
Test it NowOutput:
Declaration, Instantiation and Initialization of Java Array
We can declare, instantiate and initialize the java array together by:
Let's see the simple example to print this array.
Test it NowOutput:
For-each Loop for Java Array
We can also print the Java array using for-each loop. The Java for-each loop prints the array elements one by one. It holds an array element in a variable, then executes the body of the loop.
The syntax of the for-each loop is given below:
Let us see the example of print the elements of Java array using the for-each loop.
Output:
Passing Array to a Method in Java
We can pass the java array to method so that we can reuse the same logic on any array.
Let's see the simple example to get the minimum number of an array using a method.
Test it NowOutput:
Anonymous Array in Java
Java supports the feature of an anonymous array, so you don't need to declare the array while passing an array to the method.
Test it NowOutput:
Returning Array from the Method
We can also return an array from the method in Java.
Test it NowOutput:
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
The Java Virtual Machine (JVM) throws an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if length of the array in negative, equal to the array size or greater than the array size while traversing the array.
Test it NowOutput:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 4 at TestArrayException.main(TestArrayException.java:5) 50 60 70 80
Multidimensional Array in Java
In such case, data is stored in row and column based index (also known as matrix form).
Syntax to Declare Multidimensional Array in Java
Example to instantiate Multidimensional Array in Java
Example to initialize Multidimensional Array in Java
Example of Multidimensional Java Array
Let's see the simple example to declare, instantiate, initialize and print the 2Dimensional array.
Test it NowOutput:
Jagged Array in Java
If we are creating odd number of columns in a 2D array, it is known as a jagged array. In other words, it is an array of arrays with different number of columns.
Test it NowOutput:
What is the class name of Java array?
In Java, an array is an object. For array object, a proxy class is created whose name can be obtained by getClass().getName() method on the object.
Test it NowOutput:
Copying a Java Array
We can copy an array to another by the arraycopy() method of System class.
Syntax of arraycopy method
Example of Copying an Array in Java
Test it NowOutput:
Cloning an Array in Java
Since, Java array implements the Cloneable interface, we can create the clone of the Java array. If we create the clone of a single-dimensional array, it creates the deep copy of the Java array. It means, it will copy the actual value. But, if we create the clone of a multidimensional array, it creates the shallow copy of the Java array which means it copies the references.
Output:
Printing original array: 33 3 4 5 Printing clone of the array: 33 3 4 5 Are both equal? false
Addition of 2 Matrices in Java
Let's see a simple example that adds two matrices.
Test it NowOutput:
Multiplication of 2 Matrices in Java
In the case of matrix multiplication, a one-row element of the first matrix is multiplied by all the columns of the second matrix which can be understood by the image given below.

Let's see a simple example to multiply two matrices of 3 rows and 3 columns.
Test it NowOutput:
Related Topics
1) Java Program to copy all elements of one array into another array
2) Java Program to find the frequency of each element in the array
3) Java Program to left rotate the elements of an array
4) Java Program to print the duplicate elements of an array
5) Java Program to print the elements of an array
6) Java Program to print the elements of an array in reverse order
7) Java Program to print the elements of an array present on even position
8) Java Program to print the elements of an array present on odd position
9) Java Program to print the largest element in an array
10) Java Program to print the smallest element in an array
11) Java Program to print the number of elements present in an array
12) Java Program to print the sum of all the items of the array
13) Java Program to right rotate the elements of an array
14) Java Program to sort the elements of an array in ascending order
15) Java Program to sort the elements of an array in descending order
16) Find 3rd Largest Number in an Array
17) Find 2nd Largest Number in an Array
18) Find Largest Number in an Array
19) Find 2nd Smallest Number in an Array
20) Find Smallest Number in an Array
21) Remove Duplicate Element in an Array
22) Add Two Matrices
23) Multiply Two Matrices
24) Print Odd and Even Number from an Array
25) Transpose matrix
26) Java Program to subtract the two matrices
27) Java Program to determine whether a given matrix is an identity matrix
28) Java Program to determine whether a given matrix is a sparse matrix
29) Java Program to determine whether two matrices are equal
30) Java Program to display the lower triangular matrix
31) Java Program to display the upper triangular matrix
32) Java Program to find the frequency of odd & even numbers in the given matrix
33) Java Program to find the product of two matrices
34) Java Program to find the sum of each row and each column of a matrix
35) Java Program to find the transpose of a given matrix
How To Create One Dimensional Array In Java
Source: https://www.javatpoint.com/array-in-java
Posted by: vangentler63.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Create One Dimensional Array In Java"
Post a Comment